DNS Compared to ENS
DNS translates domain names into IP addresses, allowing people to use familiar and easily remembered domain names instead of difficult to recall IP addresses. For example, instead of typing 142.250.64.142 into a web browser, one can simply type in google.com, and DNS will direct the user to the same location as the IP address.
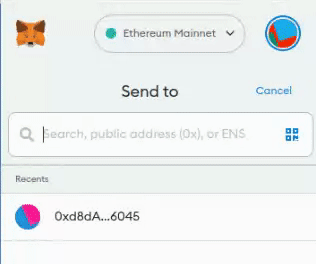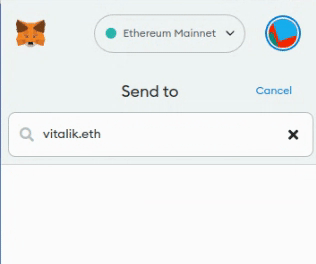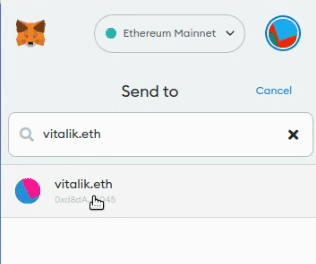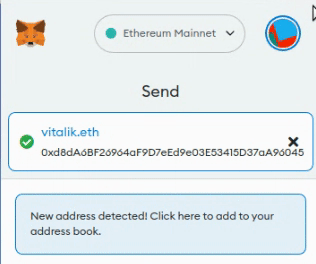
Just as DNS links domain names to IP addresses, the Ethereum Name Service (ENS) was developed to associate blockchain addresses with human-readable labels. For instance, Vitalik.eth is an ENS name that corresponds to the Ethereum blockchain address: 0xd8dA6BF26964aF9D7eEd9e03E53415D37aA96045.
ICANN Maintains Global DNS Infrastructure
If you have ever registered a website domain, that website was registered with the help of ICANN (Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers).
They are a non-profit organization based in the United States. They were formed to take over DNS responsibility from the US Government to oversee and maintain the global Internet’s Domain Name System (DNS) on the globe’s behalf.
Among other responsibilities, ICANN also manages the root zone file for top-level domains which are also known as “TLDs”. For example ICANN manages where queries resolve to for top level domains such as .com, .org, .xyz etc.
ICANN and the Blockchain
Alan Durand the CTO of ICANN writes on this issue, and provides some examples of “what it would take to use those naming systems as a DNS replacement/extension to provide the usual DNS mappings such as domain name to IP address or mail server lookup”.
You can read the “Challenges with Alternative Name Systems” whitepaper ICANN released in April of 2022.
The ENS protocol is built with DNS infrastructure in mind, thus solving many of the issues ICANN faces bridging the traditional DNS namespace to the blockchain.
It is important to note that the concept of DNS was invented in 1983, and the early engineers who built DNS could not conceive the idea of mobile smart phones, IoTA devices, advanced SHA-2 encryption, let alone decentralized and distributed network technology that is the Ethereum blockchain today.
In fact, ICANN itself was not formed until “1998 and grew out of a U.S. Government commitment to transfer the policy and technical management of the DNS”, a full decade before blockchain technology was realized in Bitcoin.
The concepts of secure and decentralized systems was not something early DNS engineers had at their disposal to build upon. It’s quite possible that had blockchain technology been known and developed then, DNS would have been built upon it because of the security and global nature of its decentralized infrastructure.