DNS records vs ENS records
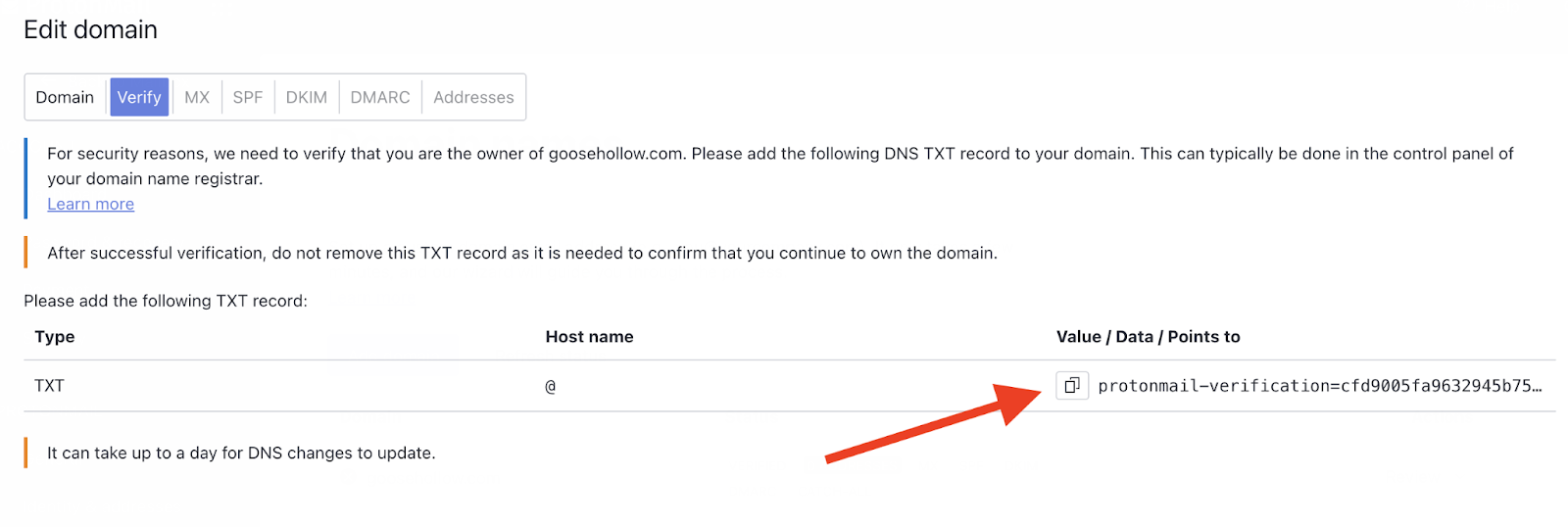
DNS records are stored in a database that maps domain names to IP addresses, indicate mail servers, or TXT records that store information. For instance, in order to add a domain to a service like Proton Mail, verification of domain ownership is necessary. This is done by adding a TXT record to the DNS records of a domain that serves as a domain verification record.
Record Storage Differences
DNS records rely on storage and security available through traditional Internet technologies outside of the blockchain. In other words, there are one or more DNS Servers responsible for storage of DNS records. An “A Record” for example is a DNS record that tells a browser where to find the IP Address of the web server where the website content is found.
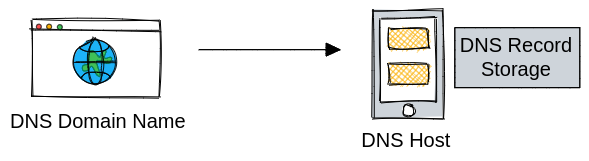
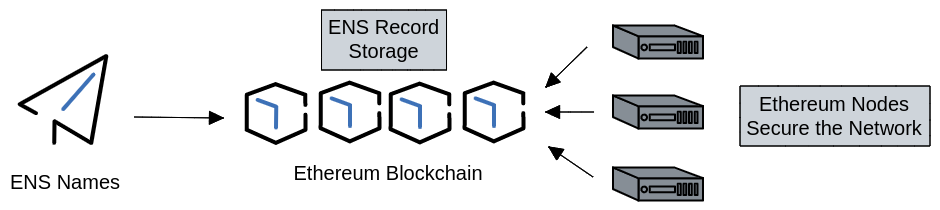
Comparatively you may wonder where ENS records are stored and updated. Because ENS is built on the Ethereum blockchain, the data records for the ENS name are not held in a centralized database. Instead, they are by default stored on the blockchain itself which is a decentralized public ledger of data. The data information for these records are resolved through smart contracts, which are also stored on the Ethereum blockchain with their code open sourced.
Updating ENS Records
Management of this data is done directly by the end user by interacting with smart contracts which are programs that run on the Ethereum blockchain. Smart contracts will allow the Ethereum wallet that has “Controller” permissions to make changes to ENS records. In other words, the power and responsibility for maintaining ENS records remains in the hands of the wallet that controls the permission for updating that ENS name’s records.